By this point, you’ve already decided to reverse your hair loss. Your hair deserves to return to its natural, best self after all.
So, you must decide which option to use as there are many ways to stop and reverse hair loss. But the ones that are scientifically proven to treat male pattern baldness effectively are Finasteride and hair transplants.
They can be used separately or together depending on their benefits and how much your hair loss has progressed, so which one should you choose?
No patient should try to make such serious decisions without a doctor’s supervision, so rest assured because that’s why we’re here.
TL;DR
➡ A hair transplant is a hair restoration surgery that any patient with enough hair follicles on their head can get.
➡ Finasteride, on the other hand, is a medication used for slowing and stopping hair loss before it can even lead to baldness.
➡ Both options contain rare side effects you can avoid, take care of, or get rid of easily. But these methods and their side effect are based on different stages of a hair restoration journey.
➡ Ultimately, for best results and effectiveness, you can restore your hairline and ensure that no further hair loss will occur by combining both these methods.
In this article, I will go through all the options you have for dealing with these questions and explain which option is suited best for which situation:
Table of Contents
Let’s start with our first, obvious option, a hair transplant:
What Is a Hair Transplant? 💉
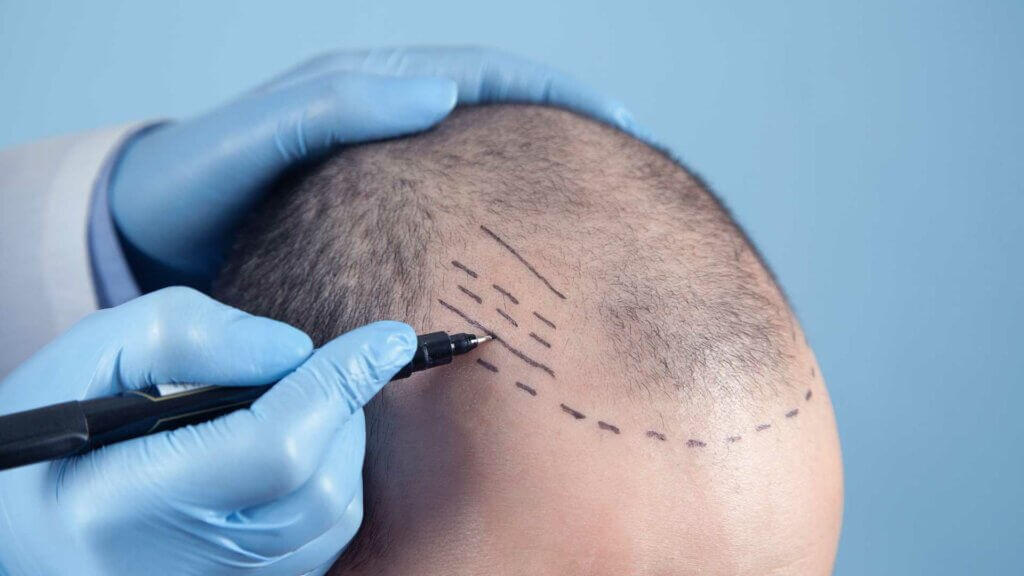
A hair transplant is a hair restoration surgery. We harvest hair follicles from your donor area to plant them in bald spots or areas where your hair is thinning.
It is a widespread treatment for androgenetic alopecia, more commonly known as male pattern baldness (MPB). You can choose different hair transplant methods depending on how far your MPB has progressed, how many follicles remain on your scalp, and with which option you’re most comfortable.
These details are crucial factors, so you must inform your doctor about them. Depending on these factors, you can conclude which option is best suited for you or whether a hair transplant is the best option for your MPB.
Who can or should get a hair transplant?
Patients from all backgrounds are generally suited for hair transplant, but to decide on its effectiveness and whether it is necessary, you must consider three things:
- Hair transplants require follicles, so the number of hair follicles you have in your head that aren’t affected by MPB will heavily influence the outcome. For best results, your donor area should be at least equal to the balding area.
- In some cases, we can guess that patient’s body will likely reject the hair transplant after the surgery based on biological factors such as age. So, ideally, patients between the ages of 25-65 are best suited for this operation as age strongly affects whether your hair is thick enough to survive the transplant.
- A hair transplant is best suited for patients who show a clear sign of developed baldness rather than being at the early ages of hair loss. There are several signs to look for to understand whether your hair is balding, such as being able to see your scalp in the mirror, changing hair lines, and losing more hair than usual every day.
💡Overall, aside from these factors, whether you are comfortable with getting surgery is a factor that we highly value as well. So, as we never tire of reminding this essential factor, it is always the safest option to talk to your doctor before making a decision.
Who can’t or shouldn’t get a hair transplant?
Aside from necessary positive criteria, some other reasons may instead cause you to be not eligible for a hair transplant, such as:
❗Patients who do not have enough hair grafts that contain the required number of hair follicles to be harvested. It can be due to the donor area being smaller than the balding area or a condition that actively destroys a patient’s hair follicles, such as scarring alopecia.
❗Patients who are outside the ideal age gap, especially those under the age of 25 as in those ages, balding is in its early, evolving, and aggressive era.
In those critical talks with your doctor that we keep reminding you about, you will likely learn about these factors that influence the transplant’s effectiveness.
Speaking of which, how effective are they exactly?
Hair transplant effectiveness
With their high popularity and dozens of studies and examples to back it up, hair transplants have been proven to work as the most successful hair loss treatment.
Hundreds of thousands of new people successfully get hair transplants and begin their new life with shiny hair every year. The transplants are so successful that 37% of patients underwent a hair transplant surgery solely to improve their social lives, and 34.7% of patients have done the same to increase their professional life.
Research shows that getting a hair transplant is so tempting and beneficial to improve your life because those who continue to live with hair loss are at a higher risk for developing social phobia, anxiety disorder, social phobia, or even paranoid disorders.
As for determining the success of hair transplants, researchers or clinical doctors trying to determine their statistics use the method of measuring how much of the transplanted hair fully grows back. A study made in 2017 found that approximately 80% of transplanted hairs fully grow back in the first four months.
As for a long-term examination, a study made in 2016 focused on observed hair transplant patients for up to 3 years post-surgery. At the end of this observation, researchers surveyed the patients’ overall satisfaction based on their healing situation, hair growth in the transplanted areas, and overall satisfaction with their surgeries. The survey results were absolute satisfaction for patients, as their average score was 7.8 on a scale of 0 to 10.
Due to their success, hair transplants have become such a standard part of our life nowadays that even many famous people have started getting hair transplants. One of the most notable of those famous individuals is the entrepreneur Elon Musk.
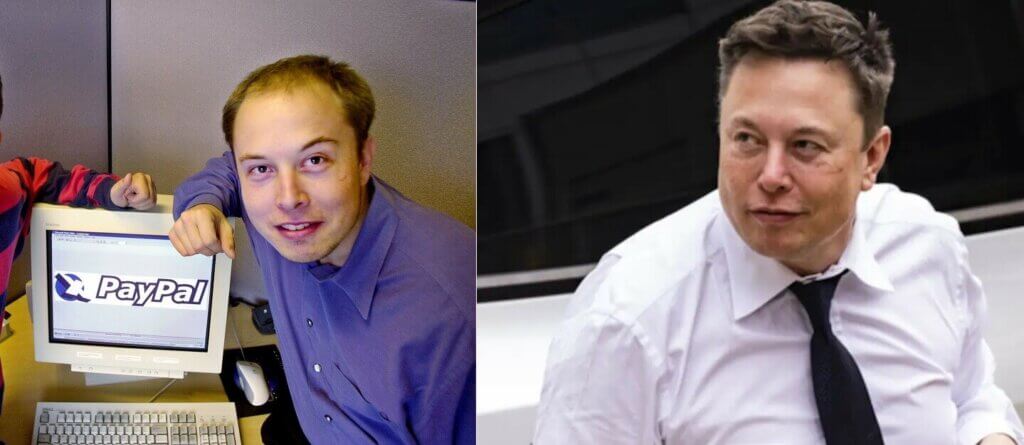

Compared to his appearance from 20 years ago, we can see a drastic improvement in his hair. Even more interesting, his transplanted hair stays fully intact even after all those years without the slightest distortion in 2022. It is a clear example of how transplanted hair can last for decades if carefully and correctly maintained.
But, to be quite frank, finding the right clinic with a dermatologist that values and observes its patients post-surgery can be tricky. That is why, although they are rare, specific risks, infections, and side effects can occur:
Hair transplant risks and side effects
Although they are rare, hair transplant does contain risks. In our field, we observe that these risks appear as inevitable side effects when an inexperienced doctor, a hair transplant clinic without a dermatologist, or a doctor who doesn’t care about patients enough to educate, inform and thoroughly survey them about their medical background is present.
In complete, here are the side effects of hair transplantations:
💠 Scars: Patients can encounter different scars around their scalp, which can vary based on hair transplant methods. You can experience tiny scars around surgical sites in FUE or linear scars around the donor site in FUT. One fundamental thing that most clinics do not tell you is that in the year 2022, no hair transplant surgery is completely “scarless.” So, although we can guarantee that your scars’ visibility will significantly diminish and get smaller with more caring doctors and modern options, you should prepare yourself for this side effect.
💠 Infections: We can see this as the worst-case scenario. And though they appear in less than 1% of the patients, according to a study, getting infections is still a genuine possibility, as it is in every other medical operation. Still, in most cases, this scenario contains only mild conditions, which we can easily treat with antibiotics or by washing the scalp.
💠 Swellings: One other common side effect is experiencing swellings around the forehead, eyelids, and face. Swellings usually begin 2-3 days after the surgery but only last for three days on average. Their heaviness, however, differs drastically between the patients. Although some experience only minimal to mild swellings, others can have a much harder time. Once it happens, specific ways to minimize it can be used, such as applying cold compresses or intaking supplementary steroids.
💠 Shock loss: Hair transplant is a stressful process for you and your scalp that just had hair follicles physically extracted and transplanted into it. So, it is entirely natural for your body to react to this stress, and when the result of this stress appears in the form of a sudden hair loss in the transplanted area, we call it “shock loss.” That is what usually happens a few weeks after the surgery. But do not worry; in almost all cases, shock loss is not permanent, and around 6-8 months after the surgery, your new hair will fill the parts that fell during the shock loss too. Thus, new hair will have grown in the place of the fallen grafts.
💠 Loss of sensation: In most cases, after the initial healing period, a loss of sensation and numbness can be present to replace pain and discomfort in the recipient and donor areas. This side effect is, just like others, only temporary, as after 2-3 weeks following the surgery, most of the sensation will return to the scalp. However, complete recovery can take much longer, so it is normal for patients to experience slight numbness around the scalp for 6-8 months post-surgery.
💠 Scabs, pain, and redness on the scalp: In the first following the surgery, during your initial healing process, you will experience intense pain, tightness, and overall discomfort around your scalp. That is normal, which is why painkillers are prescribed for this period. Furthermore, your body will react to the stress of the surgery by releasing various fluids such as blood and edema that quickly dries up after being released and show up on your scalp as scabs, crust, or general redness pumped to your scalp. This whole process is your body’s natural healing process, so it must be taken positively as a sign of progress. However, be careful with reading your body’s cues, and if these effects persist after a week post-surgery, immediately contact your doctor as an infection can be in place.
💠 Itching and bleeding around donor and recipient areas: These effects can occur possibly because of your body’s natural reactions. However, if the results continue to show themselves after passing the first week or if they get very severe, you should consult your doctor.
In short, most of these side effects appear either because of not continuing the communication with the patients for further information after the surgery or because of an inexperienced doctor not showing enough attention, such as having insufficient knowledge about the patient or not entirely informing the patient about the procedures.
To avoid such problems, you need a dermatologist in a clinic because hair transplantation is an innate medical practice. Ideally, not only do we want to quickly help you treat these side effects if they occur but also we want to ensure that they do not occur at all.
And although surgery is the most important, known, and critical point of a hair transplant (and your hair’s health in general in the long term), its process does not end with surgery alone. The pre-surgery and post-surgery processes are vital. They are so important that in some cases of early ages in MPB, certain supplement drugs become a life-saver to the point that people have started seeing them as a complete alternative to hair transplantation.
One of which is Finasteride:
What Is Finasteride? 💊
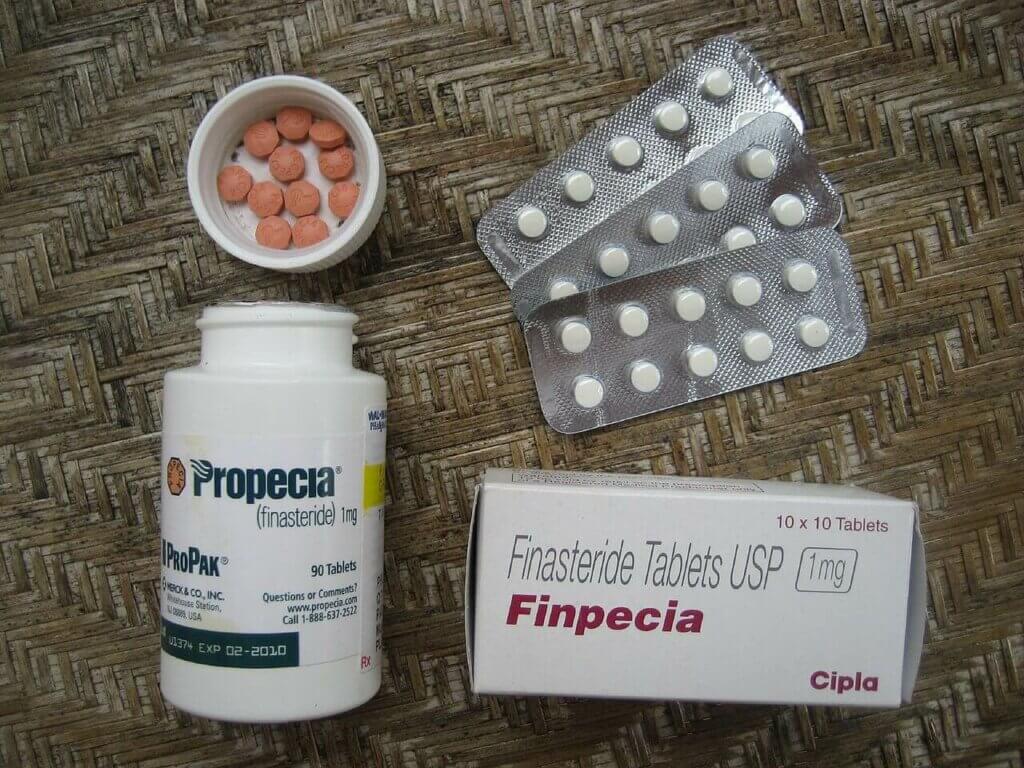
Usually appearing under its brand name Propecia, Finasteride is one of the most prominent supplement medications used in treating MPB. It is an FDA-approved, topical oral medication you can get with your doctor’s prescription. Its most known use is slowing down or preventing and reverting hair loss’s effects.
To understand Finasteride, you must understand its usage. Finasteride is a supplement drug, usually prescribed for supporting the primary treatment, such as a hair transplant surgery, generally until a year after the treatment has passed. And this is where the medication starts to shine because while hair transplants do nothing to protect the rest of your that wasn’t planted, Finasteride completely prevents it from balding.
Other than that, depending on how progressed a patient’s MPB is, it can be used alternatively:
Who can or should use Finasteride?
There are two types of patients who should consider using Finasteride:
1 – Patients who have hair loss in some parts of their heads are at an early age:
Usually, a hair transplant is not immediately suggested to every patient who shows the slightest sign of hair loss. Instead, we first recommend that patients look for any external reason such as smoking, alcohol consumption, high-stress levels, or improper diet that may be causing this process to begin. Dealing with these factors is a great way to stop or naturally slow hair loss.
In this process, one option that you can hear from your doctor upon consulting is using Finasteride. Suppose your hair is still gradually losing despite cutting out those external sources. In that case, Finasteride can help as its primary use is preventing the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is the main reason your body loses hair.
As this hormone gets produced, it causes your hair to get thinner over time and fall out. So, if resolving other factors such as stress hasn’t reduced the DHT levels in your head, you can use Finasteride to do so and save your hair from being completely bald before it is too late.
2 – Patients who are planning to or have already undergone surgery but do not wish to lose further hair and end up getting another one:
In advanced stages of balding, Finasteride can do little as it works by protecting your head from losing more follicles, from your hair getting thinner, and as a result causing your hair to return to its healthy, natural view.
But if an area in your head has completely balded, Finasteride cannot make hair regrow from this area as there aren’t any hair follicles left to protect. So, in this case, you will have to get a hair transplant surgery by doctors extracting hair from other parts of your head that still has hair. But what if those areas start slowly to lose hair as well?
Finasteride’s secondary important use is ensuring that your remaining hair stays strong. As it is advised that Finasteride should be used before and after the surgery, its benefit is ensuring that you will maintain your existing amount of hair until the surgery and continuing to protect the areas outside the effects of surgery after the transplant is finished.
If patients see their hair slowly stop losing more hair without, before and after a hair transplant surgery, we can conclude that it was successful.
So, let’s check on how effective Finasteride is at its job:
Finasteride effectiveness
Studies showing Finasteride’s effectiveness and reliability are so many and vary so much in their different objectives and patient backgrounds that we could go back to decades ago to find an entirely new approach to determine its effectiveness.
One prominent example is a clinical study from 1999 that was made on 1879 patients with MPB over the case of 24 months. This study’s strategy for determining the treatment’s effectiveness is giving the patients 1 mg of Finasteride a day orally and observing them for two years to see any increase in hair growth. And impressively, 66% of patients who used it for two years showed a significant increase in hair growth. Furthermore, 83% of patients showed no signs of further hair loss after two years.
“What about a study focusing on Finasteride’s effectiveness after a hair transplant?”
To answer that question, and since clinical studies may create bias in people, a more recent, modern, and global study was made in 2005 to specify Finasteride’s effectiveness. A group of dermatologists, with the lead of Dr. Matt Leavitt, conducted a study that lasted for 48 weeks on 79 different global patients. These patients were from around the world and selected between the ages of 25 and 45, so they were ideal candidates. After using 1 mg of Finasteride a day, visible increases in frontal scalp hair after the transplant were recorded for 94% of patients.
But one definitive thing that these studies have discovered was Finasteride comes with a few side effects:
Finasteride risks and side effects
The main risk of Finasteride is that its side effects, although relatively rare, are in a topic that instantly concerns any patient: Sexual side effects.
These rare but technically possible sexual side effects are:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased sex drive
- Ejaculation disorder
- Reduction in sperm number
The possibility of a sexual side effect appearing because of an oral drug can be scary, but its safety guarantee also lies in the same place.
Since Finasteride is not a one-time treatment like an injection but a daily dose of pills, so stopping and completely reversing its side effects is possible.
How? By stopping using it.
As research shows, these serious side effects are rare; when they appear, they appear mildly, and in the cases of severe consequences, they are completely reversible if you stop using Finasteride.
Besides, in most cases, these side effects are triggered by another disease or condition. So, once you safely inform your doctor about factors such as these, you should be clear on deciding whether you will get a hair transplant or start using Finasteride:
Hair Transplants vs. Finasteride
Now that we have gone through the uses and benefits of both methods, it should become clear that although they get close, their focuses are pretty different.
But to see which one is more effective at filling out its part, let’s look at them through some key points:
Cases of success and their results
According to a study, the number of patients who showed progress in hair growth through Finasteride is significantly higher than those who underwent a successful hair transplant surgery.
On the other hand, a successful hair transplant gives more distinct and recognizable results than successful progress in hair growth through Finasteride. Here’s a great example to show how progress is much more visible in hair transplants compared to Finasteride, thanks to our confident patient Hasan:

So, one option got the numbers, the other got the looks, but what is the ideal patient for these treatments and their studies?
What is the ideal patient for each of them?
✅ Hair transplants have definitive patient criteria based on age. We do not usually recommend a hair transplant if a patient is outside the 25-65 cycle. Finasteride, on the other hand, simply works for patients who are above the age of 18.
✅ Both methods require a certain amount of hair grafts remaining in the patient’s head. If not a single area hasn’t completely lost its entire hair follicles yet, Finasteride is the option to ensure the hair stays that way or even gets better at hair growth. A hair transplant can fill the empty areas if a patient has fully bald regions in some parts but hair follicles in others.
✅ Both options work best without an existing disease or a condition that can undermine the treatment’s effectiveness.
✅ For hair transplants, the ideal patient is the one with a clear sign of developed balding. For Finasteride, the ideal patient is either a patient who wants to ensure that the parts in their hair that did not get a transplant are safe or a patient who is in the early ages of hair loss.
So, we know that these methods create different cases with different results as their ideal patients also differ. What about their costs?
Costs
The prices for hair transplants are much more affordable in Turkey than anywhere worldwide, with the average price for 2000 grafts being $2676. But these prices can go as high as $3500 to $15000 (US) in other parts of the world.
Furthermore, additional services such as transportation, hotel, equipment, or new technologies can increase this price.
Our second method is much cheaper when they are compared. Since Finasteride is a topical over-the-counter drug, its cost is very affordable. One month of supply approximately equals $20 and varies somewhat in price depending on your country.
Still, it is clear that even when a Finasteride supply of decades is used, it is still much more affordable than a hair transplant in comparison.
But aside from just money, what type of health risks can these treatments cost you?
Health risks
Seeing the result is much more critical in determining whether a hair transplant was successful. And this takes a long time, as a hair transplant that appears successful in the first four months can turn into a hair transplant failure by the end of the first year. So, the most significant risk a hair transplant has is choosing the wrong clinic and ending up with a failed after photo that shows your hair’s change.
Aside from risks connected to your doctor, you may also experience some side effects that turn into severe injuries if not immediately recognized and treated, the most prominent one being a permanent scar or, worse, an infection. As you can realize, a clinic that observes and continues to inform their patients by showing excellent care post-surgery is also essential in this situation if we wish to minimize the risks.
Finasteride’s health risks, on the other hand, are more random, reversible mild side effects. They may be rarer but are more problematic as they are primarily libido-related side effects. The essential points for undermining Finasteride’s risks are communication and education. If you inform your doctor about any existing illness or a condition you have, your doctor can tell you whether you’re suited for using Finasteride with minimal risks or not.
So, either way, it is up to your doctor’s knowledge and the value they put into you to minimize these risks.
But aside from their general/initial uses, costs, and risks that are best controlled by your doctor’s supervision, the most distinguishable difference sticks out when talking about their long-term effectiveness post-surgery:
Long-term effectiveness
This is probably where the most definitive difference between the two methods begins: Their reliability and effectiveness in the long term.
Typically, a hair transplant is permanent unless a patient’s body rejects it due to various external reasons. Alternatively, after your hair transplant surgery, you may experience hair loss from an entirely new area. In either case, an important question arises:
Which method should you use to fight hair loss in the long term after already having gotten surgery?
You could either get another hair transplant or use Finasteride. But note that both of these options are not a one-time solution. Because no matter how many times you get a hair transplant, they will never protect your native hair follicles. Furthermore, getting a new hair transplant each time a new balding area appears will exhaust your mental health and wallet. Before saying that you can mentally and physically deal with multiple sessions, remember that every surgery takes a year to conclude. So, going for numerous surgeries will mean spending a year under surgery every few years.
In other cases, getting a hair transplant more than once may not be possible as the patient’s head will not have sufficient hair follicles for a second surgery. With some of your hair follicles not surviving the surgery being quite possible, it is very unhealthy to go for multiple surgeries as you may lose your entire hair follicles and become completely bald.
When all these are combined, it becomes clear that the better method for dealing with further hair loss is Finasteride. It is cheaper, more reliable, and does not damage your hair follicles or your mental health in the long term. And its health risks only contain its side effects that are very rare, mild, and completely reversible, not as permanent as completely losing your hair.
So, which is better: Finasteride or hair transplant?
I know you come here looking for a definite answer. But honestly, there isn’t one.
Both methods are different and very effective in what they are used to treat.
Finasteride is excellent for preventing hair loss on other parts of your head that didn’t get a transplant. And a hair transplant is perfect for regions that have run out of hair follicles and become bald. After getting your first hair transplant, we can only compare their effectiveness in dealing with further hair loss. Finasteride is a better alternative than getting more hair transplants in this contest as it is more reliable, affordable, and safe in the long run.
Expert Tip – use both!
After every different aspect we discussed, their effectiveness in battling further loss should not be criteria for choosing one over the other. As it is clear that they’re both beneficial in their fields, I highly recommend that you use both to support one another.
After all, not only do they not affect one another negatively, but Finasteride also increases the chances of a hair transplant ending with a successful result at the end of its first year. So, you can both save your balding area and protect your remaining hair by combining the two. That is why we combine these two methods here at UnitedCare:
Best of both worlds at UnitedCare
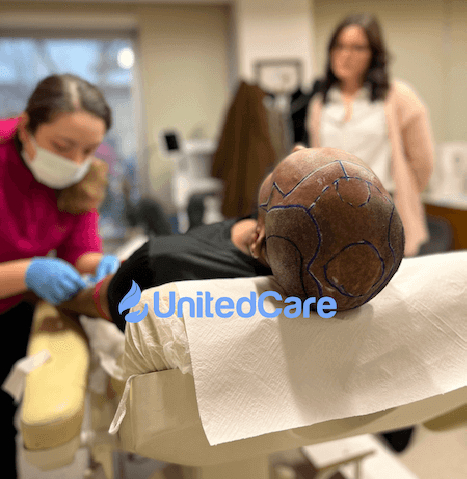
At UnitedCare, we recommend every patient to use Finasteride before going through a hair transplant to ensure its benefits start to kick in and slow down the effects of DHT. And after the surgery, as Finasteride’s actual benefits start to shine here, we continue using Finasteride to ensure that your existing hair stays healthy alongside your newly transplanted ones.
Placing Finasteride inside the hair transplant process rather than outside as a completely different method is our insurance policy for ensuring the best results in your journey towards starting your new life without worrying about balding ever again.
In short, we use the best of both worlds because your hair deserves the best the world can offer in your journey.
Ready to begin the journey? Click here to start the first step:
For best results we provide the best of both worlds.
UnitedCare‘s expert dermatologists provide you with a holistic approach to hair transplants and Finasteride:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is Finasteride a good alternative to hair transplants?
It depends on what you’re hoping to get by using Finasteride. Generally, Finasteride is used as a supplement medication for preventing hair loss on other parts of your head that did not get a hair transplant. So, in a way, it is used for further protection to guarantee you won’t lose your hair in the future. But, Finasteride will not make your hair grow in an area that has already lost its follicles completely and become bald. Usually, these two methods are compared in their effectiveness in dealing with further hair loss after getting a hair transplant. In this context, Finasteride can be an excellent alternative to getting a second hair transplant as it is more reliable, cheap, and safe in the long run. However, their usages are different, and the best option is to use them both.
Can you use Finasteride after a hair transplant?
You absolutely can and totally should. Their effects are different, but they do not diminish each other’s success. Hair transplant will deal with your balding/balded areas, and Finasteride will protect the rest of your hair from further hair loss. You can consider getting a hair transplant if you have a spot in your head that is balding or already bald. But suppose you have decided on getting one. In that case, you should undoubtedly use Finasteride before and after the hair transplant to both support the success of the hair transplant and to ensure that the rest of your hair won’t fall victim to MPB, which will result in another surgery.
Is a hair transplant more effective than Finasteride?
Statistically speaking, no. It is important to note that even though they might be used for the same reason, their effectiveness is affected by different reasons. However, it has been proven in various research by experts that those who successfully benefited from Finasteride alone are higher than those who simply got a hair transplant without a supplement drug and successfully maintained their transplanted hairs. So, when combined, statistics show us that it is more effective to use Finasteride after getting a hair transplant to combine the benefits of both worlds for better results.